| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
金属锂
CAS:7439-93-2 |
|
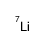 |
lithium-7
CAS:13982-05-3 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
金属锂
CAS:7439-93-2 |
|
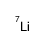 |
lithium-7
CAS:13982-05-3 |