Effects of propofol anesthesia on intradermally injected histamine phosphate in clinically normal dogs.
R A Kennis, S A Robertson, E J Rosser, J G Hauptman
文献索引:Am. J. Vet. Res. 59(1) , 7-9, (1998)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To compare skin test reactivity of ID injected histamine phosphate in clinically normal dogs that were physically restrained or anesthetized with propofol.12 clinically normal adult dogs.Nonanesthetized dogs (group 1) were restrained and shaved on the right side of the thorax. A single injection of sterile buffered saline solution (negative control) and 5 serial dilutions of histamine phosphate (0.05 ml each) were injected ID. Wheal size was measured after 15 minutes. Propofol anesthetized dogs (group 2) were shaved, and saline solution and histamine were administered ID. Wheal size was measured as for nonanesthetized dogs. Hemoglobin saturation, heart and respiratory rates, and times to sternal recumbency and standing were recorded for anesthetized dogs. Twenty-four hours later, groups were reversed, and testing was repeated on the left side of the thorax.Mean wheal size was significantly (P < 0.05) less in dogs during propofol anesthesia. Heart and respiratory rates were well maintained but hemoglobin saturation decreased during the first 6 minutes of anesthesia.Although statistically significant, the difference in mean wheal size may not be clinically important. Propofol anesthesia may be used during ID skin testing in atopic dogs. Further studies to assess effects of propofol on the reactivity of ID injected aeroallergens should be performed before recommending its use.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
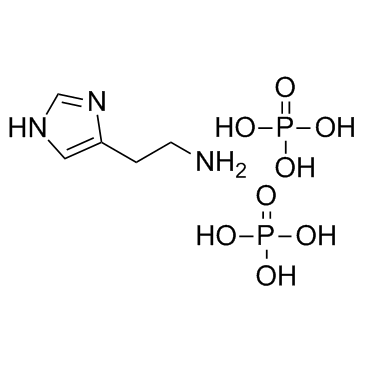 |
磷酸组胺
CAS:51-74-1 |
C5H15N3O8P2 |
|
Development of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of...
2014-11-15 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 971 , 35-42, (2014)] |
|
Validated capillary electrophoresis method for the assay of ...
1995-07-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 13(8) , 951-7, (1995)] |
|
Suppression of the early and late cutaneous allergic respons...
2001-01-01 [Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 86(1) , 44-50, (2001)] |
|
Validated capillary electrophoretic method for the quantitat...
1996-11-08 [J. Chromatogr. B, Biomed. Appl. 686(1) , 111-7, (1996)] |
|
Nasal hyperreactivity and its effect on early and late seque...
1993-01-01 [Allergy Proc. 14(4) , 273-81, (1993)] |