Effects of different crosslinking conditions on the chemical-physical properties of a novel bio-inspired composite scaffold stabilised with 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDGE).
A Nicoletti, M Fiorini, J Paolillo, L Dolcini, M Sandri, D Pressato
文献索引:J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 24(1) , 17-35, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Serious cartilage lesions (Outerbridge III, IV) may be successfully treated with a three-layered gradient scaffold made by magnesium-doped hydroxyapatite and type I collagen, manufactured through a bio-inspired process and stabilised by a reactive bis-epoxy (1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether, BDDGE). Each layer was analysed to elucidate the effects of crosslinking variables (concentration, temperature and pH). The chemical stabilisation led to an homogeneous and aligned collagenous matrix: the fibrous structures switched to a laminar foils-based arrangement and organic phases acquired an highly coordinated 3D-organization. These morphological features were strongly evident when crosslinking occurred in alkaline solution, with BDDGE concentration of at least 1 wt%. The optimised crosslinking conditions did not affect the apatite nano-crystals nucleated into self-assembling collagen fibres. The present work allowed to demonstrate that acting on BDDGE reaction parameters might be an useful tool to control the chemical-physical properties of bio-inspired scaffold suitable to heal wide osteochondral defects, even through arthroscopic procedure.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
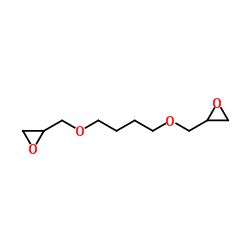 |
1,4-丁二醇二缩水甘油醚
CAS:2425-79-8 |
C10H18O4 |
|
A review of the metabolism of 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ethe...
2013-12-01 [Dermatol. Surg. 39(12) , 1758-66, (2013)] |
|
An attempt to improve diagnostics of contact allergy due to ...
2004-01-01 [Contact Dermatitis 51(5-6) , 263-72, (2004)] |
|
Chemical mutagenesis testing in Drosophila. IX. Results of 5...
1994-01-01 [Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 23(1) , 51-63, (1994)] |
|
Influence of the morphology of poly(EGDMA-co-HEMA) on the ch...
2003-01-31 [J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 55(1) , 23-36, (2003)] |
|
1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDE)-crosslinked PEI-g-imid...
2011-06-01 [Mol. Biosyst. 7(6) , 2055-65, (2011)] |