| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
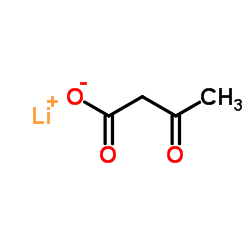 |
乙酰乙酸锂
CAS:3483-11-2 |
|
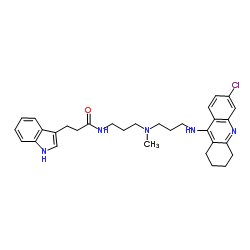 |
D-3-羟丁酸脱氢酶
CAS:9028-38-0 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙酰乙酸锂
CAS:3483-11-2 |
|
 |
D-3-羟丁酸脱氢酶
CAS:9028-38-0 |