| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
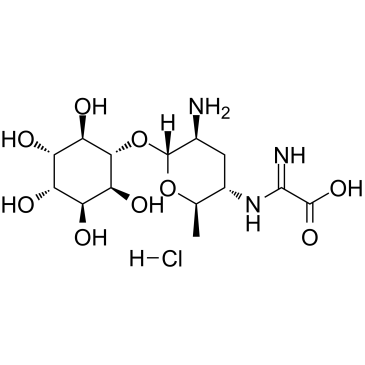 |
春雷霉素盐酸盐
CAS:19408-46-9 |
|
 |
匹美西林
CAS:32886-97-8 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
春雷霉素盐酸盐
CAS:19408-46-9 |
|
 |
匹美西林
CAS:32886-97-8 |