| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
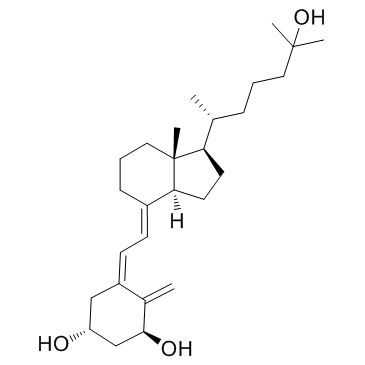 |
骨化三醇
CAS:32222-06-3 |
|
 |
咪唑安定
CAS:59467-70-8 |
|
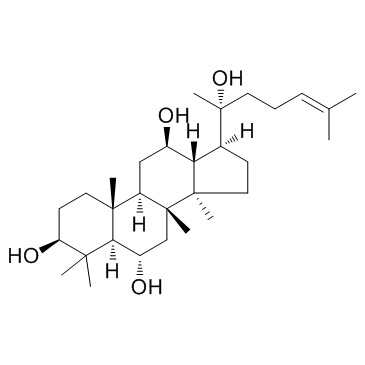 |
原人参三醇
CAS:1453-93-6 |
|
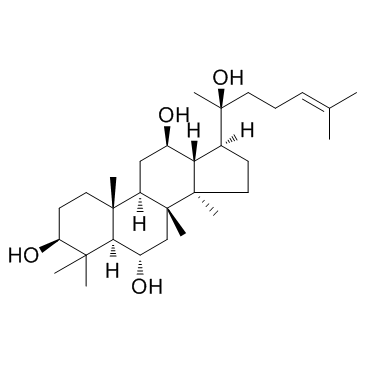 |
20(S)-原人参三醇
CAS:34080-08-5 |