Analysis of mitragynine and metabolites in human urine for detecting the use of the psychoactive plant kratom.
David Le, Melissa M Goggin, Gregory C Janis
文献索引:J. Anal. Toxicol. 36(9) , 616-25, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The leaves of the South Asian plant kratom are described as having stimulating effects at low doses, and opiate-like analgesic and euphoric effects at high doses. A long history of use and abuse has led to the classification of kratom as a controlled substance in its native Thailand and other South Asian countries. However, kratom is not controlled in the United States, and the ready availability of kratom has led to its emergence as an herbal drug of abuse. With the growing popularity of kratom, efficient procedures are needed to detect kratom use. In the current study, both ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry methods have been developed and validated for monitoring the major alkaloids and metabolites found in urine following kratom use. The primary unique alkaloid mitragynine is quantified in human urine from 1.00-500.00 ng/mL using mitraphylline as an internal standard. In addition, two metabolites (5-desmethylmitragynine and 17-desmethyldihydromitragynine) and the related active, alkaloid 7-hydroxy-mitragynine, are simultaneously qualitatively monitored. The presence of analytes are confirmed by an information-dependent acquisition-enhanced product ion procedure generating full fragmentation data used to positively identify detected analytes. The validated method has been utilized for clinical and forensic analyses of urine for the detection of kratom use.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
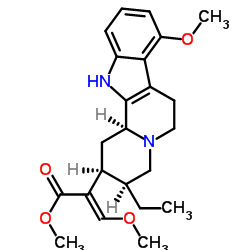 |
帽柱木碱盐酸盐
CAS:4098-40-2 |
C29H33N5O11 |
|
A drug fatality involving Kratom.
2013-01-01 [J. Forensic Sci. 58 Suppl 1 , S278-9, (2013)] |
|
Orally active opioid compounds from a non-poppy source.
2013-06-27 [J. Med. Chem. 56(12) , 4840-8, (2013)] |
|
Determination of mitragynine in plasma with solid-phase extr...
2010-07-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 397(5) , 2023-30, (2010)] |
|
A simple HPLC-DAD method for the detection and quantificatio...
2013-03-10 [Forensic Sci. Int. 226(1-3) , 183-7, (2013)] |
|
Total syntheses of mitragynine, paynantheine and speciogynin...
2012-12-28 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 48(100) , 12243-5, (2012)] |