Halogenated phospholipids regulate secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA activity.
Aleksandra Korotaeva, Elena Samoilova, Tatyana Pavlunina, Oleg M Panasenko
文献索引:Chem. Phys. Lipids 167-168 , 51-6, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA (sPLA2-IIA) is an active participant of inflammation. The enzyme destroys bacterial cell wall and induces production of biologically active lipid mediators. It is involved in various pathological processes and high serum content and activity of sPLA2-IIA are associated with adverse cardiovascular events. Study of sPLA2-IIA regulation is of great physiological and clinical importance and is necessary for better understanding of mechanisms underlying inflammation. Another major participant of inflammatory response is the enzyme myeloperoxidase (MPO) which is secreted by neutrophils in the focus of inflammation and catalyzes formation of HOCl and HOBr. Both halogenated (chloro- and bromohydrins) and oxidized lipids are formed due to interaction between HOCl and HOBr with unsaturated bonds of phospholipid acyl chains. Previously we showed that oxidized phospholipids stimulate sPLA2-IIA activity. In this study we examined the effects of chloro- and bromohydrins of 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC) on sPLA2-IIA activity. In contrast to POPC, chloro- and bromohydrins of POPC (POPC-Cl and POPC-Br, respectively) were not hydrolyzed by sPLA2-IIA. In addition, phospholipids which are sPLA2-IIA substrates, were not cleaved by the enzyme in the presence of POPC-Cl and POPC-Br. Halogenohydrins of POPC prevented the activity of both purified and serum sPLA2-IIA. Blocking effects of POPC-Cl and POPC-Br were abolished by increased concentrations of phospholipid-substrate. These results suggest that halogenated phospholipids formed in MPO-dependent reactions can be considered as a new class of biologically active compounds potentially capable of regulating sPLA2-IIA activity in the areas of inflammation and producing the effects opposite to those of oxidized phospholipids. Control over sPLA2-IIA can be useful in the therapy of diseases involving systemic inflammation.Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
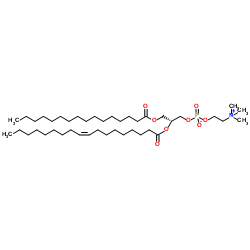 |
2-油酰-1-棕榈锡甘油-3-磷酸胆碱
CAS:26853-31-6 |
C42H82NO8P |
|
Characterizing the structure of lipodisq nanoparticles for m...
2015-01-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1848(1 Pt B) , 329-33, (2015)] |
|
Cell-penetrating antimicrobial peptides - prospectives for t...
2015-05-01 [Pharm. Res. 32(5) , 1546-56, (2015)] |
|
The cytolytic activity of vaginolysin strictly depends on ch...
2015-01-01 [Toxins (Basel.) 7(1) , 110-28, (2015)] |
|
Synthetic ion transporters can induce apoptosis by facilitat...
2014-10-01 [Nature Chemistry 6(10) , 885-92, (2014)] |
|
Role of polyol moiety of amphotericin B in ion channel forma...
2015-09-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 23 , 5782-8, (2015)] |