In-vitro digestibility and amino acid composition of soy protein isolate cross-linked with microbial transglutaminase followed by heating with ribose.
Chee-Yuen Gan, Lai-Hoong Cheng, Baharin Azahari, Azhar Mat Easa
文献索引:Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 60 Suppl 7 , 99-108, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Cross-linked soy protein isolate (SPI) gels were produced via single-treatment of SPI with microbial transglutaminase (MTG) for 5 h or 24 h, or with ribose for 2 h, or via combined-treatments of SPI with MTG followed by heating with ribose. Assessment of gel strength and solubility concluded that measures which increased protein cross-links resulted in improved gel strength; however, in most cases the digestibility and amino acid content of the gels were reduced. The combined treated gel of SPI/MTG for 24 h/ribose was more easily digested by digestive enzymes and retained higher amounts of amino acids compared with the control Maillard gels of SPI with ribose. MTG consumed lysine and glutamine and reduced the availability of amino acids for the Maillard reaction with ribose. MTG was able to preserve the nutritional value of SPI against the destructive effect of the Maillard reaction and cross-links.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
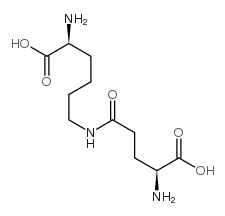 |
Epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)-lysine
CAS:17105-15-6 |
C11H21N3O5 |
|
Inhibition of transglutaminase activity reduces extracellula...
2004-11-12 [J. Biol. Chem. 279(46) , 47754-62, (2004)] |
|
Identification and quantification of epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl...
2005-04-20 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 53(8) , 2830-7, (2005)] |
|
Tissue transglutaminase: a mediator and predictor of chronic...
2004-06-15 [Transplantation 77(11) , 1667-75, (2004)] |
|
Tuft protein: protein cross-linking in enamel development.
2011-12-01 [Eur. J. Oral Sci. 119 Suppl 1 , 50-4, (2011)] |
|
Characterization of a microbial transglutaminase cross-linke...
2006-06-01 [Tissue Eng. 12(6) , 1467-74, (2006)] |