W-5 and quin 2-AM reverse the inhibitory effect of insulin on lipolysis due to dibutyryl cAMP.
H Goko, A Matsuoka
文献索引:Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 44(2) , 101-6, (1999)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The effects of W-5, a weak calmodulin antagonist, and quin 2-AM, a cell permeant calcium chelator, on lipolysis and antilipolytic activity of insulin were studied in isolated rat adipocytes. We have previously shown that W-7, a strong calmodulin antagonist, suppresses the inhibitory effect of insulin on lipolysis due to dibutyryl cAMP (Bt2cAMP) in a dose-dependent manner [H. Goko, A. Matsuoka, Diabetes Res. Clin. Prac. 19 (1993) 177-181] and verapamil, a calcium antagonist, potentiates lipolysis due to Bt2cAMP. Like W-7, W-5 suppressed the antilipolytic action of insulin on lipolysis due to Bt2cAMP in a dose-dependent manner. However, when lipolysis was potentiated with 3-isobutyryl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX), W-5 did not suppress the antilipolytic action of insulin. At the same time, like verapamil, W-5 also potentiated lipolysis due to Bt2cAMP in a dose-dependent manner. Thus W-5 has the pharmaceutical effects of both W-7 and verapamil. The chelation of intracellular Ca2+ in adipocytes with quin 2-AM also produced a dose-dependent potentiation of lipolysis due to Bt2cAMP and suppression of the antilipolytic action of insulin on lipolysis due to Bt2cAMP. These effects of quin 2-AM are the same as those of W-5. Therefore, our results suggest that the cytoplasmic Ca2+ plays a pivotal role in mediating the potentiation of lipolysis and antilipolytic action of insulin when lipolysis is induced by Bt2cAMP in rat adipocytes and that W-5 appears to exert its pharmaceutical effects through the inhibition of intracellular calcium-dependent steps other than calmodulin.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
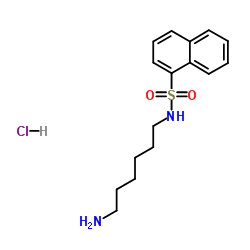 |
N-(6-氨基己基)-1-萘磺酰胺盐酸盐
CAS:61714-25-8 |
C16H23ClN2O2S |
|
Muscarinic receptor-mediated excitation of rat intracardiac ...
2015-08-01 [Neuropharmacology 95 , 395-404, (2015)] |
|
Essential role of Ca2+/calmodulin in Early Endosome Antigen-...
2003-07-01 [Mol. Biol. Cell 14(7) , 2935-45, (2003)] |
|
Occurrence of novel types of nitric oxide synthase in the si...
1995-02-06 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 207(1) , 452-9, (1995)] |
|
Regulation of immune complexes binding of macrophages by pec...
1995-02-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47(2) , 152-6, (1995)] |
|
Calmodulin-antagonists inhibit vesicular Ca2+ uptake in Dict...
1996-02-01 [Cell Calcium 19(2) , 105-11, (1996)] |