| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
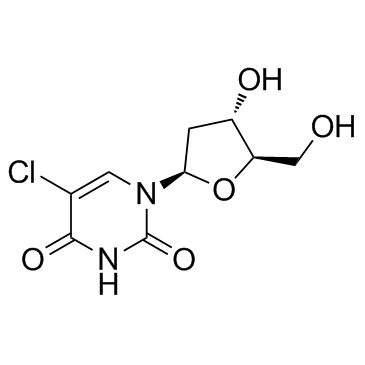 |
CldU(5-氯-2'-脱氧尿苷)
CAS:50-90-8 |
|
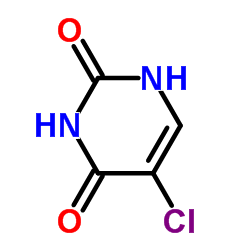 |
5-氯尿嘧啶
CAS:1820-81-1 |