Unusual metabolism of prostacyclin in infants with persistent septic pulmonary hypertension.
H Schweer, H W Seyberth, P G Kühl, C O Meese
文献索引:Eicosanoids 3(4) , 237-42, (1990)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In urine of healthy man, the major metabolite of prostacyclin is 2,3-dinor-6-oxo-prostaglandin F1 alpha. The excretion rates of this compound as well as of 2,3-dinor-thromboxane B2, a major metabolite of thromboxane A2, in two newborns with septic persistent pulmonary hypertension were about 30- to 50-fold higher than the normal range (2,3-dinor-6-oxo-prostaglandin F1 alpha: 3-15 ng/h/1.73 m2; 2,3-dinor-thromboxane B2: 8-25 ng/h/1.73 m2). The ratios of 2,3-dinor-6-oxo-13,14-dihydro-prostaglandin F1 alpha/2,3-dinor-6-oxo-prostaglandin F1 alpha in these two infants were about 100% and 800%, respectively whereas in controls the excretion of the 13,14-dihydro metabolite was found to be about 10-25% of 2,3-dinor-6-oxo-prostaglandin F1 alpha. Thus in patients with septic persistent pulmonary hypertension and extremely high excretion rates of prostacyclin and thromboxane A2 metabolites, the pattern of metabolites differs from those of healthy man.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
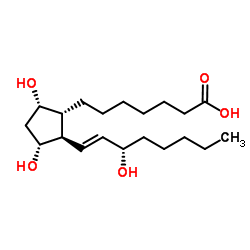 |
PGF1α(前列腺素F1α)
CAS:745-62-0 |
C20H36O5 |
|
Influence of human low density and high density lipoprotein ...
1980-12-05 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 620(3) , 352-5, (1980)] |
|
Native pentameric C-reactive protein displays more potent pr...
2006-01-01 [Atherosclerosis 184(1) , 48-52, (2006)] |
|
Long-term fenofibrate treatment impairs endothelium-dependen...
2007-07-15 [Cardiovasc. Res. 75(2) , 398-407, (2007)] |
|
The effect of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis f...
2010-01-01 [Arthritis. Res. Ther. 12(1) , R4, (2010)] |
|
Role of prostaglandins in delayed cerebral ischemia after su...
1992-01-01 [Neurosurgery 30(1) , 17-22, (1992)] |