Xenobiotics and the glucocorticoid receptor: additive antagonistic effects on tyrosine aminotransferase activity in rat hepatoma cells.
Maria Johansson, Niklas Johansson, Bert-Ove Lund
文献索引:Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 96(4) , 309-15, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Methylsulfonyl-PCBs (MeSO2-PCBs) and some fungicides were studied for their functional effects on the glucocorticoid signal transduction in the Reuber rat hepatoma H-II-E-C3 cell line. 4-Substituted MeSO2-PCBs, tolylfluanid and ketoconazole displayed antagonistic effects on dexamethasone-induced tyrosine aminotransferase specific activity (IC50 ranging from 0.7-5.1 microM), but no agonist activity. These substances also had affinity to the mouse glucocorticoid receptor in competition binding studies, indicating that the inhibition of the middle cerebral artery occlusion-activity is indeed mediated by receptor binding. Thus, substances with a structural resemblance with a methyl sulfonyl group, such as the fungicide tolylfluanid, may inhibit glucocorticoid receptor-regulated gene transcription. In co-exposure experiments with three substances, multivariate modelling showed that the inhibitory effect of 4-MeSO2-2,5,6,2',4'-pentachlorobiphenyl (4-MeSO2-CB91), 4-MeSO2-2,3,6,2',4',5'-hexachlorobiphenyl (4-MeSO2-CB149) and tolylfluanid on tyrosine aminotransferase activity was close to additive. Thus, co-exposure to such different chemicals as persistent organic pollutants and pesticides may affect cells additively. Chemical interference with the glucocorticoid hormone system therefore deserves further attention in vivo.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
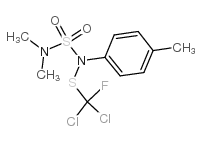 |
甲苯氟磺胺
CAS:731-27-1 |
C10H13Cl2FN2O2S2 |
|
Baby food production chain: pesticide residues in fresh appl...
2005-12-01 [Food Addit. Contam. 22(12) , 1231-42, (2005)] |
|
[Occurrence of pesticide residues in raspberries in 2000-200...
2007-01-01 [Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 58(3) , 509-13, (2007)] |
|
Exposure to fungicides in fruit growing: re-entry time as a ...
1999-01-01 [Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 60(6) , 789-93, (1999)] |
|
Processing factors and variability of pyrimethanil, fenhexam...
2003-08-01 [Food Addit. Contam. 20(8) , 728-41, (2003)] |
|
Phytotoxicity of tolylfluanid in tomatoes.
2006-01-01 [Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 71(2 Pt A) , 79-82, (2006)] |