Role of neuronal NMDA and non-NMDA glutamate receptors in medial vestibular nucleus in the regulation of respiratory rhythmogenesis in newborn rats in vitro.
N L Tyurin
文献索引:Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 148(2) , 167-70, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We studied isolated pontobulbospinal preparations from newborn rat brain. In the early postnatal period, the rostral part of the medial vestibular nucleus produces a potent inhibitory effect on neuronal structures of the bulbar respiratory center via the glutamatergic system. Microinjection of L-glutamate (50 mmol/liter) into the rostral part of the vestibular nucleus completely blocks respiratory rhythmogenesis in 0-1-day-old rat pups and reduced the frequency of generation of inspiratory discharges in 2-3-day-old rats from 8.42+/-0.68 to 2.68+/-0.32 min(-1). It was found that the leading role in the mechanism of glutamatergic modulation of the respiratory rhythmogenesis by neurons of the medial vestibular nucleus is played by NMDA and, to a lesser extent, non-NMDA glutamate receptors.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
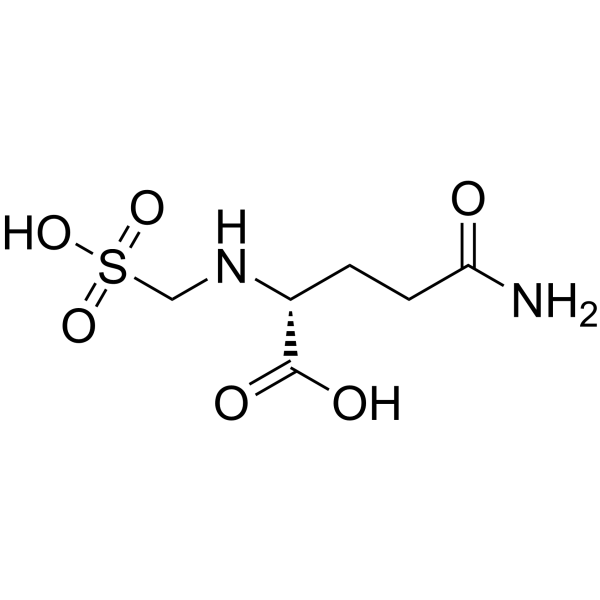 |
γ-D-谷氨酰胺基甲基磺酸
CAS:90237-02-8 |
C6H12N2O6S |
|
Effects of some excitatory amino acid antagonists on imipene...
1995-02-06 [Brain Res. 671(1) , 131-40, (1995)] |
|
Glutamate and vasopressin interact to control scent marking ...
1996-08-26 [Brain Res. 731(1-2) , 213-6, (1996)] |
|
Excitatory neurotransmitters in the lateral habenula and ped...
1992-09-25 [Brain Res. 591(2) , 209-22, (1992)] |
|
Evidence for an involvement of NMDA and non-NMDA receptors i...
1991-09-16 [Neurosci. Lett. 130(2) , 271-4, (1991)] |
|
Release of GABA from sensory neurons transduced with a GAD67...
2006-02-16 [Brain Res. 1073-1074 , 297-304, (2006)] |