Controlled evaluation of trypticase soy broth with and without gelatin and yeast extract in the detection of bacteremia and fungemia
Larry G. Reimer, L.Barth Reller, Wen-Lan L. Wang, Stanley Mirrett
文献索引:Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 8(1) , 19-24, (1987)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The addition of gelatin to blood culture media has been suggested to prevent the inhibition of Neisseria meningitidis , Neisseria gonorrhoeae , Gardnerella vaginalis , and Peptostreptococcus anaerobius that is caused by sodium polyanetholsulfonate. To determine the effect of such supplementation on the overall yield of microorganisms, we compared the yield and speed of detection of clinically important microorganisms from 5422 paired 10-ml samples of blood cultured in Trypticase soy broth (TSB) containing 0.03% sodium polyanetholesulfonate (SPS) and TSB/SPS containing 1.2% gelatin and 1.0% yeast extract (mTSB). The atmosphere of incubation (open venting unit) and ratio of blood to broth (1:5) were the same for both samples. Only cultures with adequate blood sample (≥80% of stated volume) were compared statistically. Addition of gelatin and yeast extract resulted in inhibited growth of Enterobacteriaceae ( p<0.001 ), Pseudomonas aeruginosa ( p<0.01 ), fungi fungi ( p<0.05 ), and the overall set of microorganisms encountered ( p<0.001 ). It delayed growth of Enterobacteriaceae ( p<0.001 ) but reduced the time to recover staphylococci ( p<0.02 ). Of 12 isolates of species usually inhibited by SPS, seven grew only with the addition of gelatin and yeast extract, none grew only without supplementation, and five grew in both media. Although gelatin and yeast extract may improve the yield of some specific bacteria, the routine use of these additives cannot be recommended for all blood culture media.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
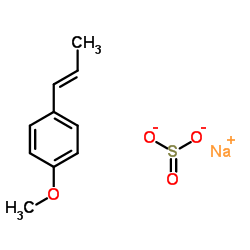 |
聚茴脑磺酸钠
CAS:55963-78-5 |
C10H12NaO4S |
|
Functional assessment of mouse complement pathway activities...
2008-01-01 [J. Immunol. Methods 419 , 25-34, (2015)] |
|
Improved amplification of microbial DNA from blood cultures ...
1998-10-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 36(10) , 2810-6, (1998)] |
|
Expanding the diagnostic use of PCR in leptospirosis: improv...
2010-08-01 [PLoS ONE 5(8) , e12095, (2010)] |
|
Use of the RapID-ANA system and sodium polyanetholesulfonate...
1990-01-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 28(1) , 108-11, (1990)] |
|
Poor performance of BACTEC NR 730 blood culture system in ea...
1989-04-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 27(4) , 654-6, (1989)] |