Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated expression of caldesmon regulates cell migration via the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton.
Taira Mayanagi, Tsuyoshi Morita, Ken'ichiro Hayashi, Kentaro Fukumoto, Kenji Sobue
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. , 31183-96, (2008)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Glucocorticoids (GCs) play important roles in numerous cellular processes, including growth, development, homeostasis, inhibition of inflammation, and immunosuppression. Here we found that GC-treated human lung carcinoma A549 cells exhibited the enhanced formation of the thick stress fibers and focal adhesions, resulting in suppression of cell migration. In a screen for GC-responsive genes encoding actin-interacting proteins, we identified caldesmon (CaD), which is specifically up-regulated in response to GCs. CaD is a regulatory protein involved in actomyosin-based contraction and the stability of actin filaments. We further demonstrated that the up-regulation of CaD expression was controlled by glucocorticoid receptor (GR). An activated form of GR directly bound to the two glucocorticoid-response element-like sequences in the human CALD1 promoter and transactivated the CALD1 gene, thereby up-regulating the CaD protein. Forced expression of CaD, without GC treatment, also enhanced the formation of thick stress fibers and focal adhesions and suppressed cell migration. Conversely, depletion of CaD abrogated the GC-induced phenotypes. The results of this study suggest that the GR-dependent up-regulation of CaD plays a pivotal role in regulating cell migration via the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
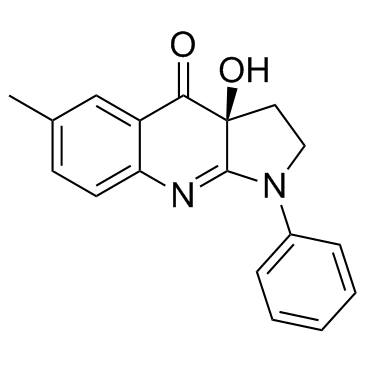 |
(-)-II型肌球蛋白
CAS:856925-71-8 |
C18H16N2O2 |
|
Stretch-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle is r...
2015-02-01 [J. Physiol. 593(3) , 645-56, (2015)] |
|
Formation of contractile networks and fibers in the medial c...
2015-01-01 [Cytoskeleton (Hoboken.) 72(1) , 29-46, (2015)] |
|
Intramolecular loop/tail interactions are essential for conn...
2010-11-01 [FASEB J. 24 , 4378-95, (2010)] |
|
Distinct cytoskeleton populations and extensive crosstalk co...
2011-04-01 [Development 138 , 1631-41, (2011)] |
|
Calcium- and myosin-dependent changes in troponin structure ...
2009-01-15 [J. Physiol. 587 , 155-63, (2009)] |