Effects of oral phosphocysteamine and rectal cysteamine in cystinosis.
W G van't Hoff, T Baker, R N Dalton, L C Duke, S P Smith, C Chantler, G B Haycock
文献索引:Arch. Dis. Child. 66(12) , 1434-7, (1991)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Diurnal variation in leucocyte cystine and the effects of equimolar single doses of oral phosphocysteamine and rectal cysteamine were studied in eight patients with cystinosis, aged 1.8-16.5 years. No significant diurnal variation in leucocyte cystine was found. Absorption of cysteamine was reduced after rectal administration compared with the oral dose: mean (SD) peak concentration 17.2 (6.3) mumol/l v 36.4 (5.5) mumol/l at 40 min and mean (SD) area under the curve 22.3 (14.3) v 59.4 (33.1) mumol/h/l. Oral phosphocysteamine significantly reduced the mean (SD) leucocyte cystine from 8.09 (0.47) to 3.26 (1.48) nmol 1/2 cystine/mg protein at three hours. At 12 hours the mean leucocyte cystine was significantly lower than the pretreatment concentration. Rectal cysteamine did not significantly reduce the mean leucocyte cystine concentration. In conclusion, phosphocysteamine suspension may be administered every 12 hours. Rectal cysteamine administration is feasible but higher doses are required before efficacy can be judged.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
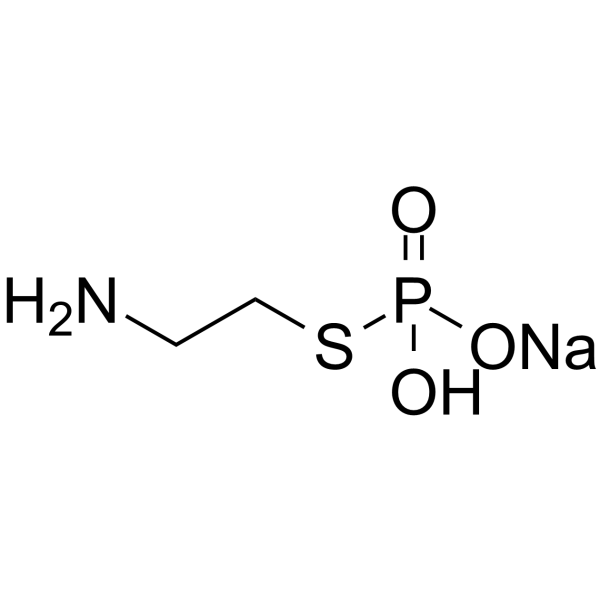 |
半胱胺S-磷酸盐 钠盐
CAS:3724-89-8 |
C2H7NNaO3PS |
|
A comparison of the effectiveness of cysteamine and phosphoc...
1988-06-01 [Pediatr. Res. 23(6) , 616-20, (1988)] |
|
The treatment of cystinosis with cysteamine and phosphocyste...
1995-12-01 [Pediatr. Nephrol. 9(6) , 685-9, (1995)] |
|
Combination small molecule PPT1 mimetic and CNS-directed gen...
2012-09-01 [J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 35(5) , 847-57, (2012)] |
|
[The effect of phenol derivatives on the antimutagenic activ...
1993-01-01 [Izv. Akad. Nauk Ser. Biol. (4) , 613-7, (1993)] |
|
[Ways of reducing the toxicity of chemotherapy of cancer of ...
1986-01-01 [Sov. Med. (5) , 24-8, (1986)] |