| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
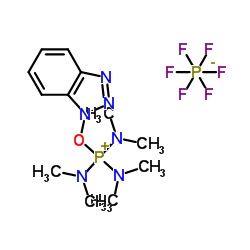 |
卡特缩合剂
CAS:56602-33-6 |
|
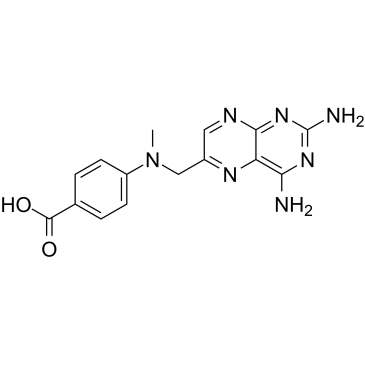 |
4-氨基-4-脱氧-10-甲基蝶酸
CAS:19741-14-1 |