Inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced receptor activation and fibroblast migration by hyaluronan activation of CD44.
Lingli Li, Carl-Henrik Heldin, Paraskevi Heldin
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. 281 , 26512-26519, (2006)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The extracellular matrix molecule hyaluronan was found to suppress platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) beta-receptor activation and PDGF-BB-induced migration of primary human dermal fibroblasts. The suppressive effect of hyaluronan was neutralized by a monoclonal antibody that specifically inhibits hyaluronan binding to its receptor CD44. Moreover, co-immunoprecipitation experiments showed that the PDGF beta-receptor and CD44 can form a complex. Interestingly, the inhibitory effect of hyaluronan on PDGF beta-receptor activation was not seen in the presence of the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor pervanadate. Our observations suggest that hyaluronan suppresses PDGF beta-receptor activation by recruiting a CD44-associated tyrosine phosphatase to the receptor.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
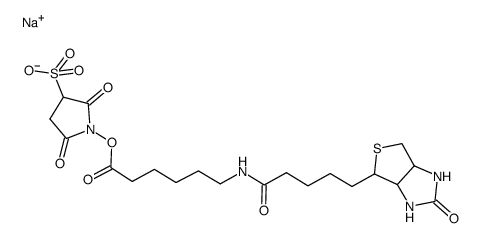 |
生物素酰氨基己酸-3-磺酸基-N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺酯
CAS:127062-22-0 |
C20H29N4NaO9S2 |
|
Dehydrogenase-modified carbon-fiber microelectrodes for the ...
1993-03-01 [Anal. Chem. 65 , 623-630, (1993)] |
|
Activation of mu-opioid receptors transfers control of Galph...
2005-03-11 [J. Biol. Chem. 280 , 8951-8960, (2005)] |
|
A screening for the occurrence of autoreactive antibodies in...
2006-02-01 [Reprod. Domest. Anim. 41(1) , 48-54, (2006)] |
|
DC-SIGN ligation on dendritic cells results in ERK and PI3K ...
2006-05-15 [Blood 107 , 3950-3958, (2006)] |
|
Proteomic approach to the identification of cell membrane pr...
2000-01-01 [Electrophoresis 21 , 460-464, (2000)] |