Molecular mechanism of codon recognition by tRNA species with modified uridine in the first position of the anticodon.
S Yokoyama, T Watanabe, K Murao, H Ishikura, Z Yamaizumi, S Nishimura, T Miyazawa
文献索引:Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 82 , 4905-4909, (1985)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Proton NMR analyses have been made to elucidate the conformational characteristics of modified nucleotides as found in the first position of the anticodon of tRNA [derivatives of 5-methyl-2-thiouridine 5'-monophosphate (pxm5s2U) and derivatives of 5-hydroxyuridine 5'-monophosphate (pxo5U)]. In pxm5s2U, the C3'-endo form is extraordinarily more stable than the C2'-endo form for the ribose ring, because of the combined effects of the 2-thiocarbonyl group and the 5-substituent. By contrast, in pxo5U, the C2'-endo form is much more stable than the C3'-endo form, because of the interaction between the 5-substituent and the 5'-phosphate group. The enthalpy differences between the C2'-endo form and the C3'-endo form have been obtained as 1.1, -0.7, and 0.1 kcal/mol (1 cal = 4.184 J) for pxm5s2U, pxo5U, and unmodified uridine 5'-monophosphate, respectively. These findings lead to the conclusion that xm5s2U in the first position of the anticodon exclusively takes the C3'-endo form to recognize adenosine (but not uridine) as the third letter of the codon, whereas xo5U takes the C2'-endo form as well as the C3'-endo form to recognize adenosine, guanosine, and uridine as the third letter of the codon on ribosome. Accordingly, the biological significance of such modifications of uridine to xm5s2U/xo5U is in the regulation of the conformational rigidity/flexibility in the first position of the anticodon so as to guarantee the correct and efficient translation of codons in protein biosynthesis.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
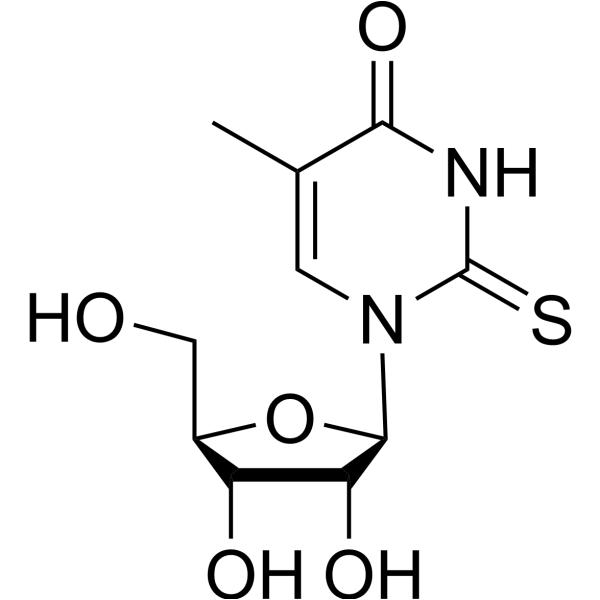 |
5-甲基-2-硫脲啶
CAS:32738-09-3 |
C10H14N2O5S |
|
CD spectra of 5-methyl-2-thiouridine in tRNA-Met-f from an e...
1976-07-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 3 , 1703-1713, (1976)] |
|
Stabilizing contributions of sulfur-modified nucleotides: cr...
2005-01-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 33 , 5297-5307, (2005)] |
|
NMR analyses on the molecular mechanism of the conformationa...
1983-06-27 [FEBS Lett. 157(1) , 95-9, (1983)] |
|
Temperature-dependent biosynthesis of 2-thioribothymidine of...
2006-01-27 [J. Biol. Chem. 281(4) , 2104-13, (2006)] |
|
Two tRNAIle1 species from an extreme thermophile, Thermus th...
1985-10-08 [Biochemistry 24(21) , 5711-5, (1985)] |