Alkaline titrations of poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC): microemulsion versus solution behavior.
Marta Airoldi, Giuseppe Gennaro, Marcello Giomini, Anna Maria Giuliani, Mauro Giustini
文献索引:J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 24 , 561-570, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
PolyGC was titrated with a strong base in the presence of increasing concentrations of NaCl (from 0.00 to 0.60M) either in water solution or with the polynucleotide solubilized in the aqueous core of reverse micelles, i.e., the cationic quaternary water-in-oil microemulsion CTAB/n-hexane/n-pentanol/water. The results for matched samples in the two media were compared. CD and UV spectroscopies and, for the solution experiments, pH measurements were used to follow the course of deprotonation. In both media the primary effect of the addition of base was denaturation of the polynucleotide, reversible by back-titration with a strong acid. In solution, the apparent pK(a) of the transition decreases with increasing the salt concentration and a roughly linear dependence of pK(a) on p[NaCl] has been found. A parallel monotonic decay with ionic strength has been found in solution for R(OH), defined as the number of hydroxyl ions required per monomeric unit of polyGC to reach half-transition. By contrast, in microemulsion, R(OH) has been found to be independent of the NaCl concentration (and 10 to 50 times lower than in solution). This result is proposed as an indirect evidence of the independence of pK(a) on the salt concentration in microemulsion, where the pH cannot be measured. A sort of buffering effect of the positive charges on the micellar wall and of their counter-ions on the ionic strength could well explain this discrepancy of behavior in the two media.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
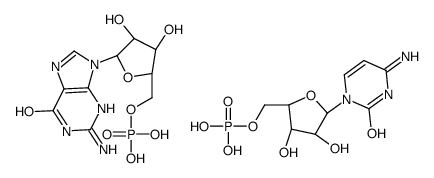 |
POLYCYTIDYLIC-POLYGUANYLIC ACID SODIUM
CAS:25280-45-9 |
C19H28N8O16P2 |
|
Oligopyrenotides: chiral nanoscale templates for chromophore...
2012-05-14 [Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 51(20) , 4905-8, (2012)] |
|
Structure and electronic spectra of DNA mini-hairpins with G...
2007-11-15 [J. Phys. Chem. B 111(45) , 13101-6, (2007)] |
|
Effect of the alkaline cations on the stability of the model...
2011-12-01 [J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 29 , 585-594, (2011)] |
|
Acid titrations of poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC) in aqueous soluti...
2006-02-01 [J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 23 , 465-478, (2006)] |
|
The CdCl2 effects on synthetic DNAs encaged in the nanodomai...
2011-07-14 [Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13 , 12293-12304, (2011)] |