Gas chromatography-electron impact-mass spectrometry (GC-EI-MS) analysis of saturated fatty acid compositions in formalin-fixed human tissues.
H Yamamoto, T Yamamoto, H Konno, F Tezuka, Y Iwasaki
文献索引:J. Neurol. Sci. 77(1) , 1-10, (1987)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Applicability of the gas chromatography-electron impact-mass spectrometry and data system (GC-EI-MS) for fatty acid analysis of formalin-fixed human tissues was evaluated by comparison of formalin-fixed and unfixed brain tissues, and the results of GC-EI-MS analyses of the formalin-fixed brain and adrenal cortex from cases with adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) and the cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome of Zellweger (ZWS) were presented. When formalin-fixed and unfixed materials were compared, a reduction of polyunsaturated fatty acids was observed after formalin fixation, while saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids remained unchanged. The chromatographic patterns of brain tissues fixed in 10% formalin for 3 days or 17 months were basically the same. In ALD, increased C26:0/C22:0 ratios in the cerebral white matter (2.05 in ALD versus 0.74 in control) and in the adrenal gland (15.2 in ALD versus 0.1 in control), and the presence of unusual very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA), longer than C29:0, were demonstrated. In the ZWS brain, all of the VLCFAs were severely depleted. Thus, formalin-fixed tissue may be a reliable subject to fatty acid analysis.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
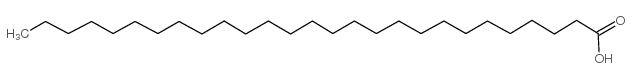 |
二十七烷酸
CAS:7138-40-1 |
C27H54O2 |
|
Fatty acid transport protein 1 can compensate for fatty acid...
2015-02-01 [J. Invest. Dermatol. 135(2) , 462-70, (2015)] |
|
Phytanic acid and very long chain fatty acids in genetic per...
1989-05-01 [J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 27(5) , 309-14, (1989)] |
|
Characterization of wax esters, triglycerides, and free fatt...
1986-06-01 [J. Invest. Dermatol. 86(6) , 700-5, (1986)] |
|
Membrane microviscosity is increased in the erythrocytes of ...
1983-07-01 [J. Clin. Invest. 72(1) , 245-8, (1983)] |