| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
5-甲氧基水杨酸
CAS:2612-02-4 |
|
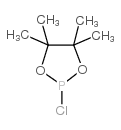 |
2-氯-4,4,5,5-四甲基-1,3,2-二噁磷杂戊环
CAS:14812-59-0 |
|
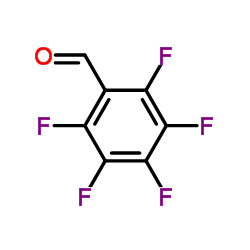 |
五氟苯甲醛
CAS:653-37-2 |