Effect of the lipid hydrolysis products on the phospholipase A2 action towards lipid monolayer.
V M Mirsky
文献索引:Chem. Phys. Lipids 70(1) , 75-81, (1994)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The effect of lauric acid (LA) and lysolauroyllecithin (LLL) on the hydrolysis of lipid in monolayer by phospholipase A2 from Bee venom was studied. It was found that LLL inhibits phospholipase action under both high (39 mN/m) and low (25 mN/m) surface pressure. On the other hand, LA inhibits phospholipase action under the low surface pressure (15 mN/m or 25 mN/m), but increases enzyme activity under high surface pressure (39 mN/m). This activating effect can be suppressed by high ionic strength of the aqueous subphase. It is suggested that an increase of the negative surface charge of the lipid monolayer, followed by an increase of the local concentrations of the positively charged enzyme and calcium near the monolayer is a coupling factor between fatty acid accumulation and phospholipase activation. Such an autocatalytic process can only occur when the substrate is organised into monolayer, bilayer or micelles, therefore it can be considered as a reason for the substrate activation and induction time before lipid hydrolysis.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
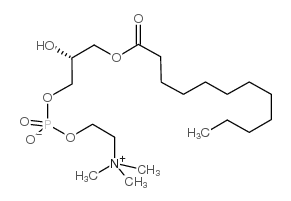 |
L-A-溶血磷酰脂胆碱
CAS:20559-18-6 |
C20H42NO7P |
|
Conformation of phospholipids. Crystal structure of a lysoph...
1980-03-05 [J. Mol. Biol. 137(3) , 249-64, (1980)] |
|
The polar group conformation of a lysophosphatidylcholine an...
1980-03-05 [J. Mol. Biol. 137(3) , 265-82, (1980)] |
|
Pulmonary surfactant: an interdisciplinary approach.
1984-12-01 [J. Appl. Physiol. 57(6) , 1613-24, (1984)] |
|
The hemifusion intermediate and its conversion to complete f...
1995-09-01 [Biophys. J. 69(3) , 922-9, (1995)] |
|
Interactions between bovine myelin basic protein and zwitter...
1990-02-06 [Biochemistry 29(5) , 1142-7, (1990)] |