Denopamine stimulates alveolar fluid clearance via cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in rat lungs.
Xiu Gu, Zheng Wang, Jin Xu, Sumiko Maeda, Makoto Sugita, Motoyasu Sagawa, Hirohisa Toga, Tsutomu Sakuma
文献索引:Respirology 11(5) , 566-71, (2006)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The objective of this study was to test the hypothesis that cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) plays a role in beta(1)-adrenergic agonist-stimulated alveolar fluid clearance.Isotonic 5% albumin solutions containing different pharmacological agents were instilled into the alveolar spaces of the isolated rat lungs. The lungs were inflated with 100% oxygen at an airway pressure of 7 cm H(2)O and placed in a humidified incubator at 37 degrees C. Alveolar fluid clearance was estimated by the progressive increase in the albumin concentration over 1 h. To test the hypothesis, we determined whether CFTR Cl(-) channel inhibitors (glibenclamide and CFTR(inh)-172) inhibited the effect of denopamine, a beta(1)-adrenergic agonist, on stimulation of alveolar fluid clearance in the isolated rat lungs.Denopamine increased alveolar fluid clearance in a dose-dependent manner. Atenolol, a beta(1)-adrenergic antagonist, abolished the effects of denopamine on stimulation of alveolar fluid clearance. Although glibenclamide alone or CFTR(inh)-172 alone did not change basal alveolar fluid clearance, these CFTR inhibitors inhibited the effect of denopamine on alveolar fluid clearance.CFTR plays a role in beta(1)-adrenergic agonist-stimulated alveolar fluid clearance in rat lungs.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
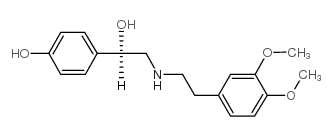 |
R(-)-去甲胺
CAS:71771-90-9 |
C18H23NO4 |
|
Binding pockets of the beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenergic recep...
1999-11-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 56 , 875-885, (1999)] |
|
Regioselective glucuronidation of denopamine: marked species...
2005-03-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 33(3) , 403-12, (2005)] |
|
Vascular responses to beta-adrenoceptor subtype-selective ag...
2001-02-01 [J. Auton. Pharmacol. 21(1) , 7-13, (2001)] |
|
Denopamine, a selective beta1-receptor agonist and a new cor...
2002-01-01 [Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 18(7) , 407-13, (2002)] |
|
Modulation of L-type Ca current by denopamine, a nonparenter...
1996-10-01 [Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 354(4) , 437-43, (1996)] |