In yeast, Ca2+ and octylguanidine interact with porin (VDAC) preventing the mitochondrial permeability transition.
Manuel Gutiérrez-Aguilar, Victoriano Pérez-Vázquez, Odile Bunoust, Stéphen Manon, Michel Rigoulet, Salvador Uribe
文献索引:Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1767(10) , 1245-51, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In yeast, Ca(2+) and long chain alkylguanidines interact with mitochondria modulating the opening of the yeast mitochondrial unspecific channel. Mammalians possess a similar structure, the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. The composition of these pores is under debate. Among other components, the voltage-dependent anion channel has been proposed as a component of either pore. In yeast from an industrial strain, octylguanidine and calcium closed the yeast mitochondrial unspecific channel. Here, the effects of the cations Ca(2+) or octylguanidine and the voltage-dependent anion channel effector decavanadate were evaluated in yeast mitochondria from either a wild type or a voltage-dependent anion channel deletion laboratory strain. It was observed that in the absence of voltage-dependent anion channel, the yeast mitochondrial unspecific channel was desensitized to Ca(2+), octylguanidine or decavanadate but remained sensitive to phosphate. It is thus suggested that in yeast mitochondria, the voltage-dependent anion channel has a cation binding site where Ca(2+) and octylguanidine interact, conferring cation sensitivity to the yeast mitochondrial unspecific channel.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
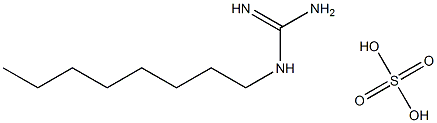 |
1-辛基胍半硫酸盐
CAS:21409-35-8 |
CH3(CH2)7NHC(=NH)NH2·1/2H2SO4 |
|
Inactivation of mitochondrial permeability transition pore b...
2000-04-01 [J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 32(2) , 193-8, (2000)] |
|
Environment-selective synergism using self-assembling cytoto...
1988-12-01 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 37(23) , 4505-12, (1988)] |
|
Myocardial protective effect of octylguanidine against the d...
2005-01-01 [Mol. Cell Biochem. 269(1-2) , 19-26, (2005)] |
|
Effects of octylguanidine on heart activity: 2. Mechanical c...
1980-03-30 [Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 56(6) , 625-9, (1980)] |
|
Effects of octylguanidine on heart activity: 1. Electrical c...
1980-03-30 [Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 56(6) , 619-24, (1980)] |