Comparative toxicity of methyl isocyanate and its hydrolytic derivatives in rats. I. Pulmonary histopathology in the acute phase.
K Jeevaratnam, S Sriramachari
文献索引:Arch. Toxicol. 69(1) , 39-44, (1994)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The present study describes the acute histopathological changes induced by methyl isocyanate (MIC) in the lungs of rats at 24 h after a single exposure to varied concentrations/doses of MIC by inhalation and subcutaneous (s.c.) routes and also delineates the effects due to the hydrolytic derivatives of MIC, viz., methylamine (MA) and N,N'-dimethyl urea (DMU). MIC, either inhaled or administered s.c., resulted in a wide range and extent of histopathological changes in the lungs, proportional to the exposure concentration/dose. The salient, effects of inhaled MIC are acute necrotizing bronchitis of the entire respiratory tract accompanied by varying degrees of confluent congestion, hyperemia and interstitial and intra-alveolar edema, while MIC administered s.c. led to prominent vascular endothelial damage, congestion and severe interstitial pneumonitis with apparently normal bronchial epithelium; and intra-alveolar edema only with the high dose. The only noteworthy lesion produced by MA and DMU (to some extent) was interstitial pneumonitis, suggesting their possible involvement in the subsequent inflammatory response of MIC. Except, for the endothelial changes, the overall spectrum of the histopathological lesions is quite comparable to those observed in the lungs of Bhopal victims during the acute phase.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
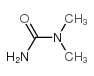 |
N,N-二甲基脲
CAS:598-94-7 |
C3H8N2O |
|
A synthesis of phosphorylated dioxohexahydropyrimidines from...
2010-11-01 [Mol. Divers. 14(4) , 617-20, (2010)] |
|
Utilization of wheat straw for the preparation of coated con...
2012-07-18 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(28) , 6921-8, (2012)] |
|
Denaturation behavior of alpha-chymotrypsinogen A in urea an...
1994-04-01 [J. Protein Chem. 13(3) , 323-31, (1994)] |
|
Effect of urea, dimethylurea, and tetramethylurea on the pha...
2002-02-01 [Chem. Phys. Lipids 114(2) , 149-57, (2002)] |
|
Apparent specific volumes of some dipeptides (containing L-v...
1992-05-01 [Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 39(5) , 415-8, (1992)] |