Human phenylalanine monooxygenase and thioether metabolism.
Boontarika Boonyapiwat, Barry Panaretou, Ben Forbes, Stephen C Mitchell, Glyn B Steventon
文献索引:J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 61(1) , 63-7, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The substrate specificity of wild-type human phenylalanine monooxygenase (wt-hPAH) has been investigated with respect to the mucoactive drug, S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine and its thioether metabolites. The ability of wt-hPAH to metabolise other S-substituted cysteines was also examined.Direct assays of PAH activity were by HPLC with fluorescence detection; indirect assays involved following disappearance of the cofactor by UV spectroscopy.wt-hPAH catalysed the S-oxygenation of S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine, its decarboxylated metabolite, S-methyl-L-cysteine, and both their corresponding N-acetylated forms. However, thiodiglycolic acid was not a substrate. The enzyme profiles for both phenylalanine and S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine showed allosteric kinetics at low substrate concentrations, with Hill constants of 2.0 and 1.9, respectively, for the substrate-activated wt-hPAH. At higher concentrations, both compounds followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics, with non-competitive substrate inhibition profiles. The thioether compounds, S-ethyl-L-cysteine, S-propyl-L-cysteine and S-butyl-L-cysteine were all found to be substrates for phenylalanine monooxygenase.Phenylalanine monooxygenase may play a wider role outside intermediary metabolism in the biotransformation of dietary-derived substituted cysteines and other exogenous thioether compounds.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
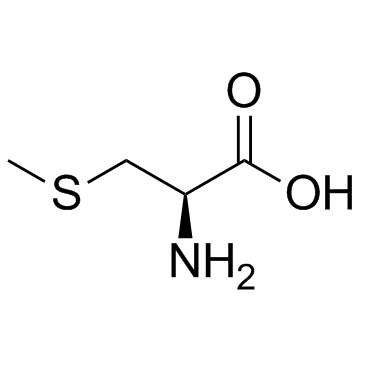 |
S-甲基-L-半胱氨酸
CAS:1187-84-4 |
C4H9NO2S |
|
Selective Allosteric Inhibition of MMP9 Is Efficacious in Pr...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0127063, (2015)] |
|
Cysteine amide adduct formation from carboxylic acid drugs v...
2015-10-01 [Pharmazie 70 , 678-83, (2015)] |
|
Synthesis and biological evaluation of L-cysteine derivative...
2007-07-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 , 3921-4, (2007)] |
|
Prebiotic synthesis of methionine and other sulfur-containin...
2011-06-01 [Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 41(3) , 201-12, (2011)] |
|
Metabolome analysis revealed increase in S-methylcysteine an...
2010-12-10 [J. Biol. Chem. 285(50) , 39160-70, (2010)] |