Exceptionally long-term persistence of DNA adducts formed by carcinogenic aristolochic acid I in renal tissue from patients with aristolochic acid nephropathy.
Heinz H Schmeiser, Jöelle L Nortier, Rajinder Singh, Gonçalo Gamboa da Costa, Jacques Sennesael, Elisabeth Cassuto-Viguier, Damien Ambrosetti, Sandrine Rorive, Agnieszka Pozdzik, David H Phillips, Marie Stiborova, Volker M Arlt
文献索引:Int. J. Cancer 135(2) , 502-7, (2014)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Aristolochic acid (AA) causes aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN), first described in women in Belgium accidently prescribed Aristolochia fangchi in a slimming treatment, and also Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN), through probable dietary contamination with Aristolochia clematitis seeds. Both nephropathies have a high risk of urothelial cancer, with AA being the causative agent. In tissues of AAN and BEN patients, a distinct DNA adduct, 7-(deoxyadenosin-N6-yl)-aristolactam I (dA-AAI), has been detected. DNA adducts can be removed through DNA repair, they can result in mutations through erroneous DNA replication or they can cause cell death. The dA-AAI adduct induces AT to TA transversions in the tumor-suppressor TP53 gene in experimental systems, matching TP53 mutations observed in urothelial tumors from AAN cancer cases. Using thin-layer chromatography 32P-postlabeling and mass spectrometric analysis we report the detection of dA-AAI in renal DNA from 11 Belgian AAN patients over 20 years after exposure to AA had ceased. Our results showed that dA-AAI is an established biomarker of AA exposure, and that this biomarker can be demonstrated to be persistent decades after a distinct AA exposure. Further, the persistence of dA-AAI adducts appears to be a critical determinant for the AA mutational fingerprint frequently found in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes recently identified by whole genome sequencing of AA-associated urothelial tumors. The potential for exposure to AA worldwide is high; the unprecedented long-term persistence of dA-AAI provides a useful long-term biomarker of exposure and attests to the role of AA in human urothelial malignancy.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
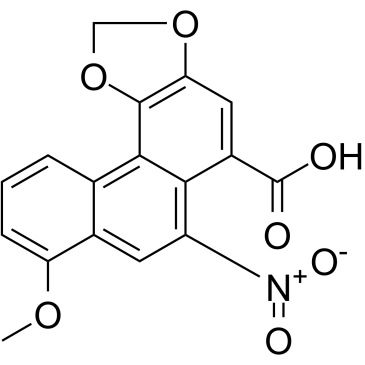 |
马兜铃酸A
CAS:313-67-7 |
C17H11NO7 |
|
Bardoxolone methyl (BARD) ameliorates aristolochic acid (AA)...
2014-03-01 [Toxicology 318 , 22-31, (2014)] |
|
Baicalin Protects Mice from Aristolochic Acid I-Induced Kidn...
2015-01-01 [Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 16454-68, (2015)] |
|
Association of blood lead and mercury with estimated GFR in ...
2013-08-01 [Occup. Environ. Med. 70(8) , 545-51, (2013)] |
|
Harpalycin 2 inhibits the enzymatic and platelet aggregation...
2012-01-01 [BMC Complement Altern. Med. 12 , 139, (2012)] |
|
Increased expression of p21WAF1/CIP1 in kidney proximal tubu...
2015-01-15 [Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 308(2) , F122-30, (2015)] |