| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
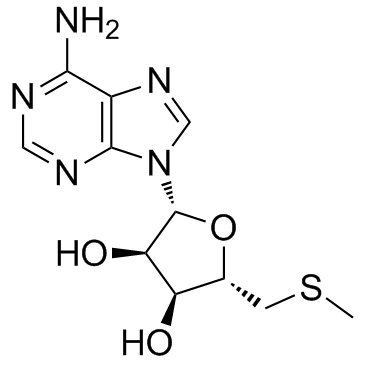 |
5′-脱氧-5′-(甲硫基)腺苷
CAS:2457-80-9 |
|
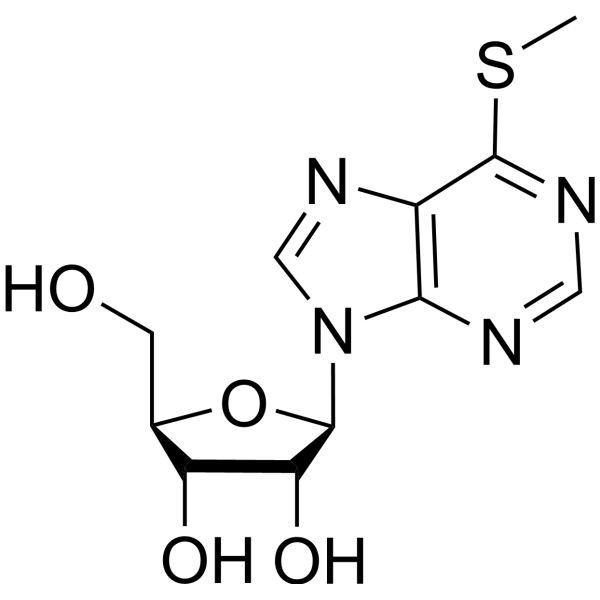 |
6-(甲硫基)-9-β-D-呋喃核糖-9H-嘌呤
CAS:342-69-8 |