Reduction of site-specific CYP3A-mediated metabolism for dual angiotensin and endothelin receptor antagonists in various in vitro systems and in cynomolgus monkeys.
Hongjian Zhang, Donglu Zhang, Wenying Li, Ming Yao, Celia D'Arienzo, Yi-Xin Li, William R Ewing, Zhengxiang Gu, Yeheng Zhu, Natesan Murugesan, Wen-Chyi Shyu, W Griffith Humphreys
文献索引:Drug Metab. Dispos. 35(5) , 795-805, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
2-{Butyryl-[2'-(4,5-dimethyl-isoxazol-3-ylsulfamoyl)-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]-amino}-N-isopropyl-3-methyl-butyramide (BMS-1) is a potent dual acting angiotensin-1 and endothelin-A receptor antagonist. The compound was subject to rapid metabolic clearance in monkey and human liver microsomes and exhibited low systemic exposure and marked interanimal variability in cynomolgus monkeys after p.o. administration. The variability pattern was identical to that of midazolam given p.o. in the same monkeys, as measured by area under the curve and Cmax values, suggesting that CYP3A-mediated metabolism might play a role in the rapid clearance and observed interanimal variability. Subsequent in vitro metabolism studies using human liver microsomes and cDNA-expressed human cytochrome P450 (P450) enzymes revealed that BMS-1 was a CYP3A4 substrate and was not metabolized by other human P450 enzymes. Mass spectral and NMR analyses of key metabolites led to the identification of the dimethyl isoxazole group as a major metabolic soft spot for BMS-1. Replacement of the 4-methyl group on the isoxazole ring with halogens not only improved overall metabolic stability but also decreased CYP3A-mediated hydroxylation of the isoxazole 5-methyl group. As exemplified by 2-{butyryl-[2'-(4-fluoro-5-methyl-isoxazol-3-ylsulfamoyl)-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]-amino}-N-isopropyl-3-methyl-butyramide (BMS-3), a fluorinated analog of BMS-1, the structural modification resulted in an increase in the systemic exposure relative to previous analogs and a dramatic reduction in interanimal variability in the monkeys after p.o. administration. In addition, BMS-3 could be metabolized by both CYP2C9 and CYP3A4, thus avoiding the reliance on a single P450 enzyme for metabolic clearance. Integration of results obtained from in vitro metabolism studies and in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluations enabled the modulation of site-specific CYP3A-mediated metabolism, yielding analogs with improved overall metabolic profiles.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
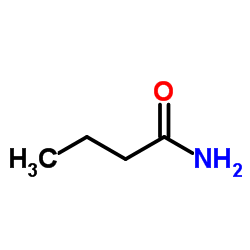 |
丁酰胺
CAS:541-35-5 |
C4H9NO |
|
Novel N-phenyl-substituted thiazolidinediones protect neural...
2014-08-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 350(2) , 273-89, (2014)] |
|
Bioconversion of butyronitrile to butyramide using whole cel...
2007-03-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74(3) , 535-9, (2007)] |
|
Synthesis of uniform protein-polymer conjugates.
2005-01-01 [Biomacromolecules 6(6) , 3380-7, (2005)] |
|
A microreactor for the study of biotransformations by a cros...
2009-04-01 [Biotechnol. J. 4(4) , 510-6, (2009)] |
|
Synthesis of N4-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-...
2001-04-23 [Carbohydr. Res. 331(4) , 439-44, (2001)] |