Signal transduction in islet hormone release: interaction of nitric oxide with basal and nutrient-induced hormone responses.
A Salehi, F Parandeh, I Lundquist
文献索引:Cell. Signal. 10(9) , 645-51, (1998)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We examined the relation between the islet NO system and islet hormone secretion induced by either the non-glucose nutrient alpha-ketoisocaproic acid (KIC) or, in some experiments, glucose. KIC dose dependently stimulated insulin but inhibited glucagon secretion. In a medium devoid of any nutrient, the NO synthase (NOS)-inhibitor N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) induced an increase in basal insulin release but a decrease in glucagon release. These effects were evident also in K+-depolarised islets. KIC-induced insulin release was increased by L-NAME. This increase was abolished in K+-depolarised islets. In contrast, glucose- induced insulin release was potentiated by L-NAME after K+ depolarisation. The intracellular NO donor hydroxylamine dose dependently inhibited KIC-stimulated insulin release and reversed KIC-induced suppression of glucagon release. Our data suggest that islet hormone secretion in a medium devoid of nutrients is greatly affected by the islet NO system, whereas KIC-induced secretion is little affected. Glucose-induced insulin release, however, is accompanied by increased NOS activity, the NOS-activating signal being derived from the glycolytic-pentose shunt part of glucose metabolism. The observed NO effects on islet hormone release can proceed independently of membrane-depolarisation events.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
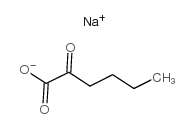 |
2-酮己酸 钠盐
CAS:13022-85-0 |
C6H9NaO3 |
|
Calcium uptake by bovine epididymal spermatozoa is regulated...
1989-04-01 [Biol. Reprod. 40(4) , 744-51, (1989)] |
|
Inhibition studies on LDH isoenzyme purified from Uromastix ...
1996-01-01 [J. Enzym. Inhib. 10(3) , 187-93, (1996)] |
|
Lactate dehydrogenase-C4 is involved in heparin- and NADH-de...
2002-04-01 [Andrologie 34(2) , 91-7, (2002)] |
|
GC-MS profiling of urinary organic acids evaluated as a quan...
1996-10-01 [Clin. Chem. 42(10) , 1609-15, (1996)] |
|
The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insuli...
1981-09-18 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 677(1) , 32-8, (1981)] |