Agents and Actions
1990-04-01
A modified radioimmunoassay for the detection of histamine release in vivo and in vitro in man.
E S Assem, D K Osei
文献索引:Agents Actions 30(1-2) , 287-90, (1990)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Histamine (Hi) release in vitro or in vivo in man was measured by variants of a radioimmunoassay (RIA) procedure. Hi released from isolated basophils was converted enzymically to N-tau-methylhistamine (NMH) which was then measured by a very sensitive RIA. This modified RIA was compared with the standard spectrofluorometric assay and was found to have additional advantages in certain applications. RIA of NMH in plasma was found to be of value in acute medical conditions of obscure aetiology.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
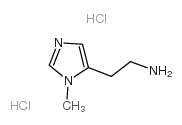 |
3-甲基组胺二盐酸盐
CAS:36475-47-5 |
C6H13Cl2N3 |
相关文献:
更多...
|
A liquid chromatographic method for the determination of his...
2007-10-01 [Arch. Pharm. Res. 30(10) , 1350-7, (2007)] |
|
Confirmation of biological effects of high dilutions. Effect...
2008-01-01 [Inflamm. Res. 57 Suppl 1 , S27-8, (2008)] |
|
Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric assay to measure urin...
[J. Chromatogr. A. 567(2) , 289-98, (1991)] |
|
Effect of histamine antagonists on myocardial carcinine meta...
1990-10-01 [J. Surg. Res. 49(4) , 293-7, (1990)] |
|
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry assay for determination...
2009-02-01 [Am. J. Vet. Res. 70(2) , 167-71, (2009)] |