Evaluation of matrix effects in metabolite profiling based on capillary liquid chromatography electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
Christoph Böttcher, Edda V Roepenack-Lahaye, Edith Willscher, Dierk Scheel, Stephan Clemens
文献索引:Anal. Chem. 79(4) , 1507-13, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The coupling of liquid chromatography to electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry can be a powerful tool for metabolomics, i.e., the comprehensive detection of low molecular weight compounds in biological systems. There have, however, been doubts about the feasibility and reliability of this approach, because LC-MS--especially with electrospray ionization--can be subject to matrix effects. We evaluated matrix effects for our metabolomics platform in three ways: (i) postextraction addition of a set of reference compounds to different complex biological matrixes to determine absolute and relative matrix effects, (ii) postcolumn infusion of two reference compounds, and (iii) mixing of two complex matrixes. Our data demonstrate that there are indeed significant absolute matrix effects when comparing highly divergent samples. However, relative matrix effects are negligible--unless extremely divergent matrixes are compared--and do not compromise the relative quantification that is aimed for in nontargeted metabolomics studies. In conclusion, employing LC-coupled ESI-QTOF-MS for metabolomics studies is feasible yet rigorous validation is necessary.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
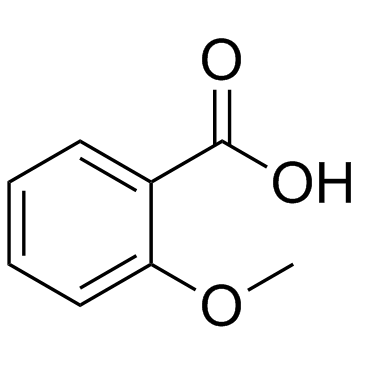 |
邻甲氧基苯甲酸
CAS:579-75-9 |
C8H8O3 |
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(...
2005-05-05 [J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005)] |
|
Endogenous salicylic acid accumulation is required for chill...
2014-10-01 [Planta 240(4) , 687-700, (2014)] |
|
Purification and properties of gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase fro...
1975-03-01 [J. Bacteriol. 121(3) , 794-9, (1975)] |
|
Effects of solute characteristics and concentration on a lyo...
1993-05-01 [Pharm. Res. 10(5) , 737-42, (1993)] |
|
[Heterocycles 39 , 47, (1994)] |