Scavenging of acetylperoxyl radicals and quenching of triplet diacetyl by beta-carotene: mechanisms and kinetics.
A Mortensen
文献索引:J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 61(1-2) , 62-7, (2001)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Beta-carotene scavenges triplet diacetyl generated by laser flash photolysis with a second-order rate constant of 9.1+/-0.9 x 10(9) M(-1) s(-1) in deaerated benzene at 20 degrees C. In the presence of oxygen diacetyl dissociates to generate acetylperoxyl radicals. It is demonstrated that diacetyl does not dissociate to any appreciable extent in the absence of oxygen. The acetylperoxyl radical is scavenged by beta-carotene with second-order rate constant 9.2+/-0.6 x 10(8) M(-1) s(-1) in aerated benzene at 20 degrees C to give an adduct between the acetylperoxyl radical and beta-carotene, whereas no evidence of oxidation of beta-carotene by the strongly oxidizing acetylperoxyl radical to give the beta-carotene radical cation is found. This adduct decays with first-order rate constant 1.35+/-0.16 x 10(3) s(-1) to give (presumably) a beta-carotene epoxide and the acetyloxyl radical.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
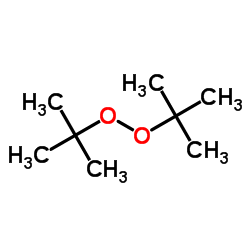 |
二叔丁基过氧化物
CAS:110-05-4 |
C8H18O2 |
|
Zwitterionic Antifouling Coatings for the Purification of Hi...
2015-11-03 [Langmuir 31 , 11895-903, (2015)] |
|
Nanothin Coculture Membranes with Tunable Pore Architecture ...
2015-10-27 [ACS Nano 9 , 10186-202, (2015)] |
|
The Fungal Exopolysaccharide Galactosaminogalactan Mediates ...
2015-10-01 [PLoS Pathog. 11 , e1005187, (2015)] |
|
Modulation of cell metabolic pathways and oxidative stress s...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0119857, (2015)] |
|
Umbilical-cord-blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded o...
2014-07-01 [Acta Biomater. 10(7) , 3007-17, (2014)] |