Dual effect of initial [K] on vascular tone in rat mesenteric arteries.
Didier X P Brochet, Philip D Langton
文献索引:Pflugers Arch. 453(1) , 33-41, (2006)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A slight increase in extracellular concentration of potassium ([K(+)](o)) can act as a vasodilator in rat mesenteric vascular bed. However, in recent years, several groups have failed to consistently observe relaxation of rat mesenteric arteries in these conditions. The aim of the present study was to provide a mechanistic understanding of this discrepancy. In rat small mesenteric arteries, 37 of 40 arteries mounted for measurement of isometric force and pre-contracted with phenylephrine (PE) did not relax when ([K(+)](o) was raised from 5.9 mM (control ([K(+)](o) to 11.2 or 21.2 mM. However, when ([K(+)](o) was briefly lowered to 1.2 mM, increasing ([K(+)](o) to between 5.9 and 41.2 mM evoked relaxation. This relaxation was not reduced by barium or by removal of the endothelium, but was abolished by 0.1 mM ouabain. Raising ([K(+)](o) from concentrations between 0 and 5.9 mM to 13.8 mM elicited a relaxation of PE-induced tone that was inversely proportional to initial ([K(+)](o). Relaxation was associated with a ouabain-sensitive hyperpolarization of smooth muscle cells. In arteries exposed to dihydroouabain (DHO), raising ([K(+)](o) from 5.9 to 13.8 mM and simultaneously washing out DHO resulted in relaxation of PE-induced force. These results suggest that only when the initial ([K(+)](o) is less than approximately 5 mM do small elevations in ([K(+)](o) evoke smooth muscle hyperpolarization and relaxation via activation of Na,K-ATPase, and not inwardly rectifying K(+) channels. Therefore, small differences in the initial ([K(+)](o) (4.6 vs 5.9 mM) can strongly influence the variations of vascular tone to increases in ([K(+)](o).
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
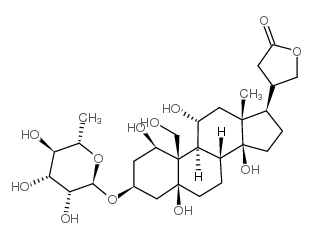 |
二氢乌本箭毒苷
CAS:1183-35-3 |
C29H46O12 |
|
Sodium-potassium-ATPase electrogenicity in cerebral precapil...
2000-07-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 279(1) , H351-60, (2000)] |
|
Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase inhibition upregulates NMDA-evoked current...
2012-08-01 [Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 26(4) , 503-12, (2012)] |
|
Contribution of cytosolic ionic and energetic milieu change ...
1998-01-01 [J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 31(1) , 146-56, (1998)] |
|
Isoform-specific function and distribution of Na/K pumps in ...
2000-11-15 [J. Membr. Biol. 178(2) , 89-101, (2000)] |
|
Novel form of LTD induced by transient, partial inhibition o...
2004-01-01 [J. Neurophysiol. 91(1) , 239-47, (2004)] |