Efficient calf thymus DNA condensation upon binding with novel bile acid polyamine amides.
Andrew J Geall, Dima Al-Hadithi, Ian S Blagbrough
文献索引:Bioconjug. Chem. 13(3) , 481-90, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Polyamine amides have been prepared from lithocholic and cholic acids (5beta-colanes) by acylation of tri-Boc-protected tetraamines spermine and thermine. These designed ligands for DNA are polyammonium ions at physiological pH. In NMR spectra, they display 14N-1H 1J = 51 Hz, 1:1:1 triplets, due to the symmetry of the R14NH(3)+ cations. The binding affinities of these conjugates for calf thymus DNA were determined using an ethidium bromide fluorescence quenching assay and compared with spermine and polylysine. DNA-binding affinities were dependent upon both salt concentration and the hydrophobicity or intermolecular bonding (facial effects) of the lipid moieties in these conjugates. Light scattering at 320 nm was used to determine DNA condensation and particle formation. The observed self-assembly phenomena are discussed with respect to DNA charge neutralization and DNA bending with loss of ethidium cation intercalation sites, ultimately leading to DNA condensation. These polyamine amides are models for lipoplex formation with respect to gene delivery (lipofection), a key first step in gene therapy.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
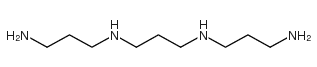 |
双3-氨基丙基-1,3-丙二胺
CAS:4605-14-5 |
C9H24N4 |
|
Heterologous expression and biochemical characterization of ...
2006-08-01 [Plant Physiol. 141(4) , 1519-32, (2006)] |
|
Identification of the unusual polyamines 3,3'-diaminodipropy...
1977-08-08 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 77(3) , 1103-7, (1977)] |
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Cu (II), Co (II) and Ni (I...
[J. Coord. Chem. 56(1) , 1-11, (2003)] |
|
Chemical features of the protein kinase CK2 polyamine bindin...
1997-02-11 [Biochemistry 36(6) , 1242-50, (1997)] |
|
Structural requirement for axonal regeneration-promoting eff...
1997-08-22 [Brain Res. 766(1-2) , 281-4, (1997)] |