Levofloxacin
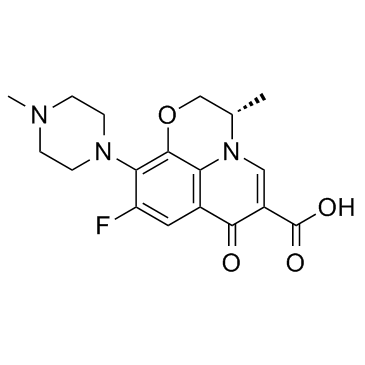
Levofloxacin structure
|
Common Name | Levofloxacin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 100986-85-4 | Molecular Weight | 361.367 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 571.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H20FN3O4 | Melting Point | 218ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 299.4±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Evaluation of a dental pulp-derived cell sheet cultured on amniotic membrane substrate.
Biomed Mater Eng 25(2) , 203-12, (2015) Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are transplanted for periodontal tissue regeneration, and the periodontal ligament (PDL) is regenerated using a cultured cell sheet. This cultured cell sheet is prepared using PDL-derived cells, growth factors, and amniotic membra... |
|
|
Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibition Improves Corneal Epithelial Innervation and Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 56(3) , 1948-55, (2015) We evaluated the effect of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibition by using 1,5-isoquinolinediol (ISO) on corneal epithelial innervation in diabetic rats.ISO (3 mg/kg, intraperitoneal) or vehicle was administered to rats with diabetes induced by strepto... |
|
|
Targeting the gyrase of Plasmodium falciparum with topoisomerase poisons.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 95 , 227-37, (2015) Drug-resistant malaria poses a major public health problem throughout the world and the need for new antimalarial drugs is growing. The apicoplast, a chloroplast-like organelle essential for malaria parasite survival and with no counterpart in humans, offers ... |
|
|
In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of heteroaryl isothiazolones against resistant gram-positive pathogens.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 1259-67, (2007) The activities of several tricyclic heteroaryl isothiazolones (HITZs) against an assortment of gram-positive and gram-negative clinical isolates were assessed. These compounds target bacterial DNA replication and were found to possess broad-spectrum activitie... |
|
|
In vitro antibacterial activities of JNJ-Q2, a new broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 , 1955-64, (2010) JNJ-Q2, a novel fluorinated 4-quinolone, was evaluated for its antibacterial potency by broth and agar microdilution MIC methods in studies focused on skin and respiratory tract pathogens, including strains exhibiting contemporary fluoroquinolone resistance p... |
|
|
Fluoroquinolone efflux by the plasmid-mediated multidrug efflux pump QacB variant QacBIII in Staphylococcus aureus.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 , 4107-11, (2010) Plasmids that carry the multidrug efflux genes qacA and qacB are widely distributed in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Although the QacA and QacB proteins are similar to each other, their respective substrate specificities may differ. We i... |
|
|
New plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone efflux pump, QepA, found in an Escherichia coli clinical isolate.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 3354-60, (2007) Plasmid-mediated Qnr and AAC(6')-Ib-cr have been recognized as new molecular mechanisms affecting fluoroquinolone (FQ) resistance. C316, an Escherichia coli strain demonstrating resistance to various FQs, was isolated in Japan. Resistance to FQs was augmented... |
|
|
Transferable resistance to aminoglycosides by methylation of G1405 in 16S rRNA and to hydrophilic fluoroquinolones by QepA-mediated efflux in Escherichia coli.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 2464-9, (2007) Plasmid pIP1206 was detected in Escherichia coli strain 1540 during the screening of clinical isolates of Enterobacteriaceae for high-level resistance to aminoglycosides. The sequence of this IncFI conjugative plasmid of ca. 100 kb was partially determined. p... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |