Ultrasound targeted CNS gene delivery for Parkinson's disease treatment
Ching-Hsiang Fan, Chung-Yin Lin, Hao-Li Liu, Chih-Kuang Yeh
Index: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.004
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
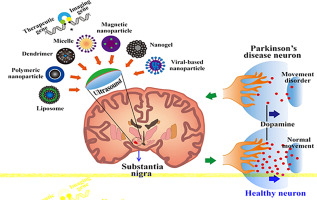
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a potent neurodegenerative disease in which a progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons eventually produces a loss of movement control and other symptoms. To date, in addition to pharmacological, non-pharmacological, and neurosurgical therapies, gene delivery has emerged as a potential therapeutic modality for PD. Effective targeted gene delivery is complicated in that gene vectors cannot penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB), thus clinical tests must rely on invasive intracerebral gene vector injection. Burst low-pressure focused ultrasound exposure with microbubbles has been demonstrated to noninvasively target and temporally open the BBB, opening new opportunities to transport large molecule substances into the brain for central nervous system (CNS) disease treatment, and raising the potential for noninvasive gene delivery for PD treatment. This paper reviews the underlying mechanism and current progress for focused ultrasound induced CNS gene delivery, and summarizes potential directions for further ultrasound-medicated PD gene therapy.
|
Gastroresistant oral peptide for fluorescence imaging of col...
2017-07-19 [10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.024] |
|
Chains of magnetosomes with controlled endotoxin release and...
2017-07-13 [10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.020] |
|
Diphtheria toxoid and N-trimethyl chitosan layer-by-layer co...
2017-07-11 [10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.017] |
|
Drug-eluting embolic microspheres for local drug delivery – ...
2017-07-11 [10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.016] |
|
Amelioration of atherosclerotic inflammation and plaques via...
2017-07-11 [10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.019] |