Experimental and DFT characterization of interphase boundaries in titanium and the implications for ω-assisted α phase precipitation
Dongdong Li, Weifeng Wan, Lvqi Zhu, Yong Jiang, Shouqi Shao, Gaojing Yang, Huiqun Liu, Danqing Yi, Shuo Cao, Qingmiao Hu
Index: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.03.056
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
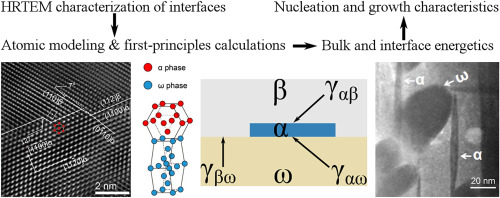
An intricate understanding of the fundamental β→α phase transformation upon the presence of metastable ω phase is vital for tailoring the multiphase microstructures of titanium and titanium alloys for various specific applications. To approach this, the structures and energetics of heterophase interfaces among α, β, and ω in titanium were thoroughly investigated, using the combination of high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and first-principles density functional theory calculations. The results strongly suggest that metastable ω does not necessarily act as the precursor of α but can reduce the energy barrier for α nucleation in β. The ω/β interfaces acts as favorable nucleation sites for α which, once forms, tends to grow favorably into the β matrix. These findings validate the ω-assisted α nucleation mechanism, and adequately rationalize many TEM observations on titanium alloys.
|
Compositional effect on microstructure and properties of NbT...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.actamat.2018.03.065] |
|
High resolution transmission electron microscopy correlated ...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.actamat.2018.03.066] |
|
Effect of heat treatment on the microstructural evolution of...
2018-04-04 [10.1016/j.actamat.2018.03.017] |
|
Fatigue deformation in a polycrystalline nickel base superal...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.actamat.2018.03.035] |
|
Deformation mechanisms of nil temperature ductile polycrysta...
2018-04-02 [10.1016/j.actamat.2018.03.064] |