FT-IR- and Raman-based biochemical profiling of the early stage of pulmonary metastasis of breast cancer in mice
Karolina Chrabaszcz, Kamila Kochan, Andrzej Fedorowicz, Agnieszka Jasztal, Elzbieta Buczek, Lisa S. Leslie, Rohit Bhargava, Kamilla Malek, Stefan Chlopicki, Katarzyna M. Marzec
Index: 10.1039/C7AN01883E
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
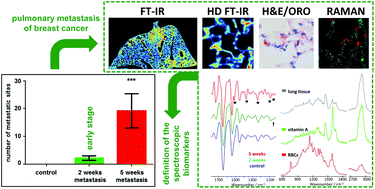
The combination of FT-IR and Raman spectroscopies allowed the biochemical profiling of lungs in the early stage of pulmonary metastasis in the murine model of breast cancer. Histological staining was used as a reference. Raman spectroscopy was especially useful in the detection and semi-quantitative analysis of the vitamin A content in lung lipofibroblasts, whereas the IR technique provided semi-quantitative information on the contents of nucleic acids, carbohydrates including glycogen, and lipids as well as changes in the secondary structures of tissue proteins. Our spectroscopic results suggest that the early phase of metastasis in the lung is characterized by a decrease in the endogenous retinoid content in combination with a decrease in the content of glycogen and lipids.
|
Self-assembly two-dimensional gold nanoparticles film for sen...
2018-04-11 [10.1039/C8AN00540K] |
|
In-vitro and ex-vivo measurements of biophysical properties ...
2018-04-11 [10.1039/C8AN00231B] |
|
Dependence of cell adhesion on extracellular matrix material...
2018-04-11 [10.1039/C8AN00429C] |
|
One-step isothermal detection of multiple KRAS mutations by ...
2018-04-11 [10.1039/C8AN00525G] |
|
Simple preparation and highly selective detection of silver ...
2018-04-10 [10.1039/C7AN02084H] |