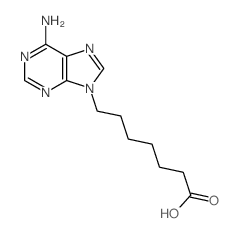
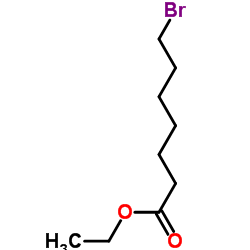
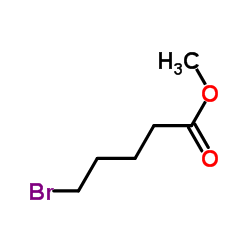
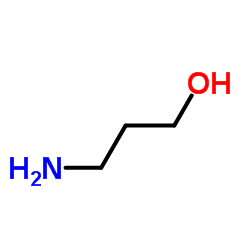
|
~% |
|
~% |
|
~% |
|
~% |
|
~68% |