| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
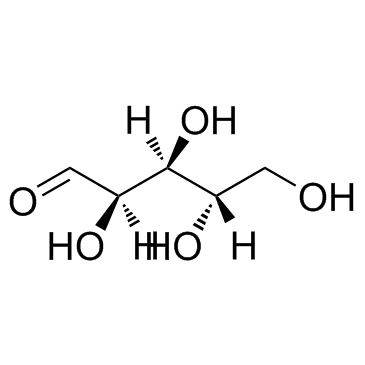 |
L-(+)-Arabinose
CAS:5328-37-0 |
|
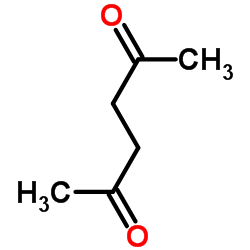 |
Acetonylacetone
CAS:110-13-4 |
|
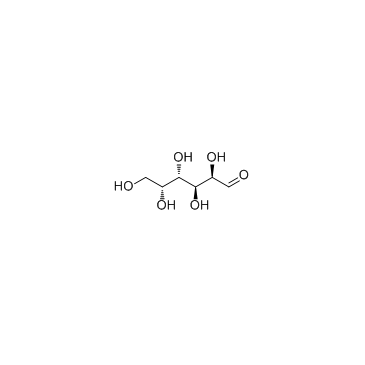 |
D-Galactose
CAS:59-23-4 |
|
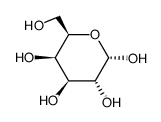 |
galactose
CAS:3646-73-9 |