| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
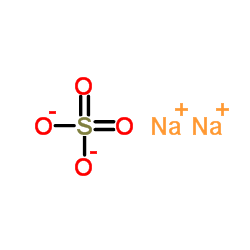 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
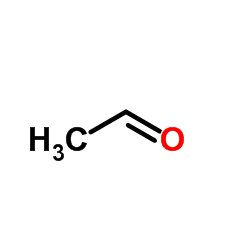 |
ch3cho
CAS:75-07-0 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
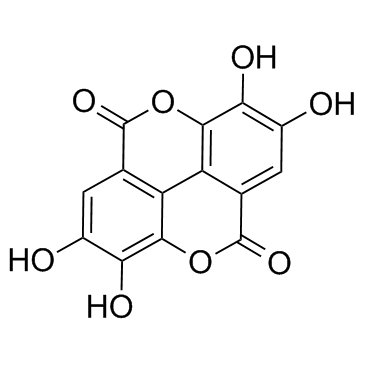 |
Ellagic acid
CAS:476-66-4 |