| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
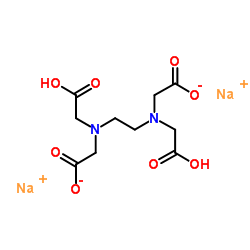 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt
CAS:139-33-3 |
|
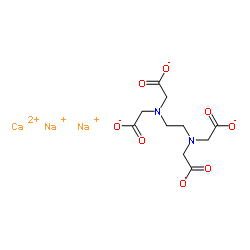 |
Disodium monocalcium EDTA
CAS:62-33-9 |
|
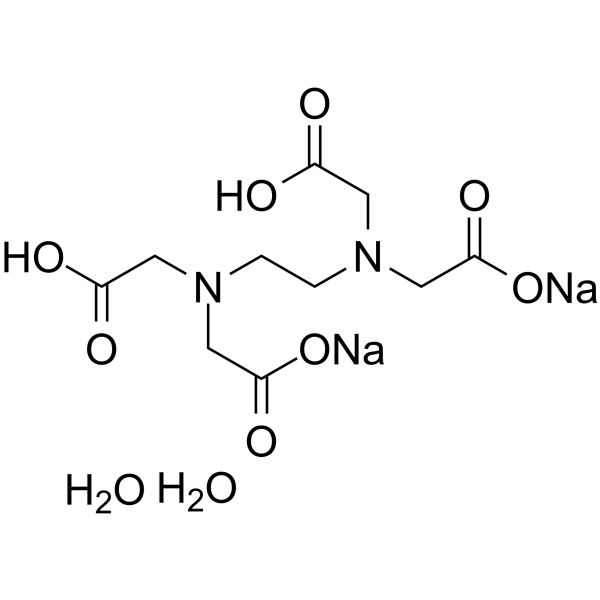 |
Disodium edetate dihydrate
CAS:6381-92-6 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |