| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
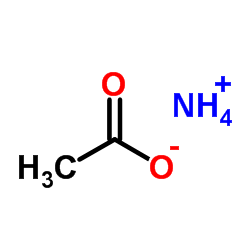 |
Ammonium acetate
CAS:631-61-8 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Aqueous ammonia
CAS:1336-21-6 |