| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
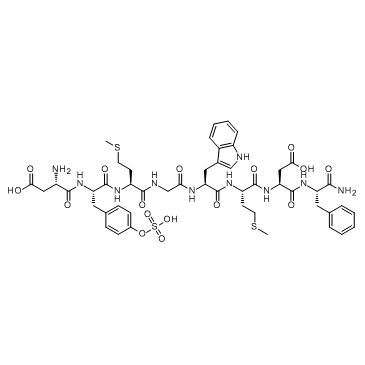 |
Cholecystokinin Octapeptide (sulfated) ammonium salt
CAS:25126-32-3 |