| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
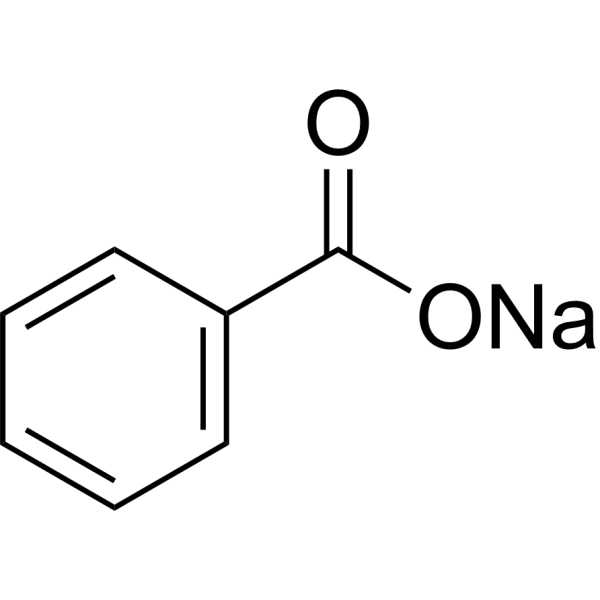 |
Sodium Benzoate
CAS:532-32-1 |
|
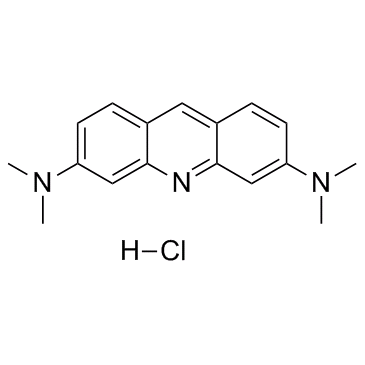 |
Acridine Orange hydrochloride
CAS:65-61-2 |
|
 |
Calf thymus DNA
CAS:91080-16-9 |