Biochemical Pharmacology
1983-04-01
Immobilization of protein molecules on liposomes. Anchorage by artificially bound unsaturated hydrocarbon tails.
V S Goldmacher
Index: Biochem. Pharmacol. 32(7) , 1207-10, (1983)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A method for the immobilization of trypsin, a hydrophilic nonmembrane protein, on a liposomal surface has been developed. The technique consists of covalent coupling of linoleoyl residues to the protein globules and consequent binding of linoleoyl trypsin to liposomes by a detergent dilution method. The immobilized protein preserved its biological functions: specific esterolytic catalytic activity and ability to bind to a macromolecular trypsin protein inhibitor. Liposomes carrying immobilized trypsin were able to sequester glucose with the same efficiency as liposomes without trypsin.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
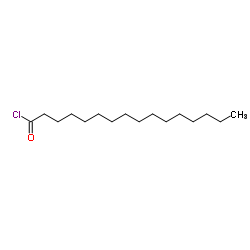 |
Palmitoyl chloride
CAS:112-67-4 |
C16H31ClO |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Establishment of LC-MS methods for the analysis of palmitoyl...
2015-07-01 [J. Lipid Res. 56 , 1370-9, (2015)] |
|
Lipophilic prodrugs of apomorphine I: preparation, character...
2015-01-01 [Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 89 , 216-23, (2015)] |
|
Use of multivariate statistical techniques to optimize the s...
2015-03-01 [Talanta 134 , 256-63, (2015)] |
|
Polymer micelle formulations of proteasome inhibitor carfilz...
2015-11-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 355 , 168-73, (2015)] |
|
Assessment of acylation routes and structural characterisati...
2014-12-15 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 28(23) , 2605-16, (2014)] |