| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Potassium
CAS:7440-09-7 |
|
 |
Ammonium nitrate
CAS:6484-52-2 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
 |
magnesium sulfate
CAS:7487-88-9 |
|
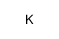 |
potassium hydride
CAS:7693-26-7 |